Certainly, Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service that helps organizations manage their devices and applications, providing mobile device management (MDM), mobile application management (MAM) and PC management capabilities. Now, You can find the list of Microsoft Intune features offered:
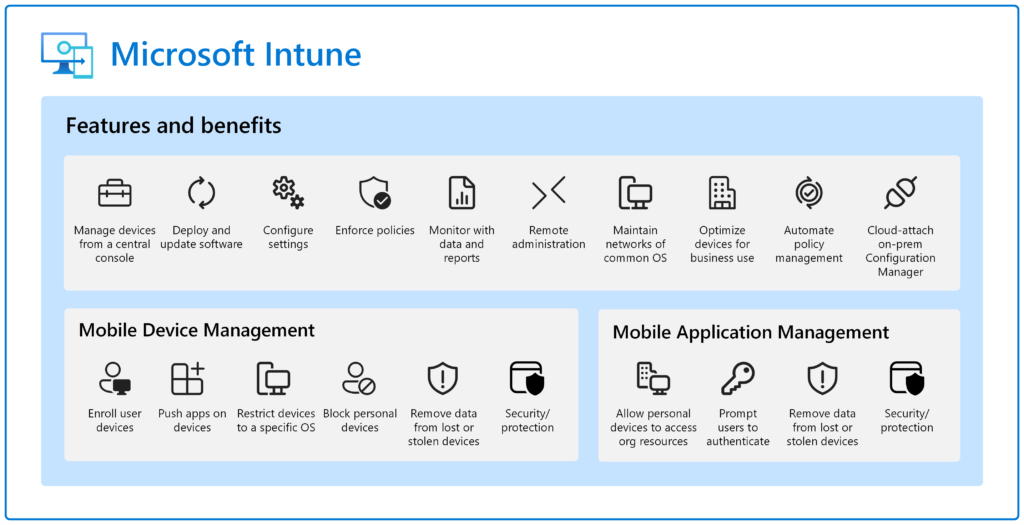
Microsoft Intune Features
Microsoft Intune offers a range of powerful features to streamline device management and enhance security in organizations. Here are the list of Microsoft intune features:
1. Endpoint Management
Microsoft Intune core capabilities includes cross-platform endpoint management. You can manage on-premises, cloud, mobile, desktop and virtual endpoints across platforms, including Windows, mac, iOS, Android, and Linux operating systems.
- Remote Actions: Administrators can perform remote actions on devices, such as locking, resetting passcodes, or wiping data, to maintain control and security over lost or stolen devices.
- Integration with Microsoft 365: Intune integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft 365 services, such as Azure Active Directory, Microsoft Endpoint Manager, and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, providing a comprehensive management solution.
2. Mobile Device Management
Intune allows administrators to manage a wide range of mobile devices, including smartphones, tablets, and Windows PCs. It supports multiple platforms such as iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS, providing centralized management capabilities.
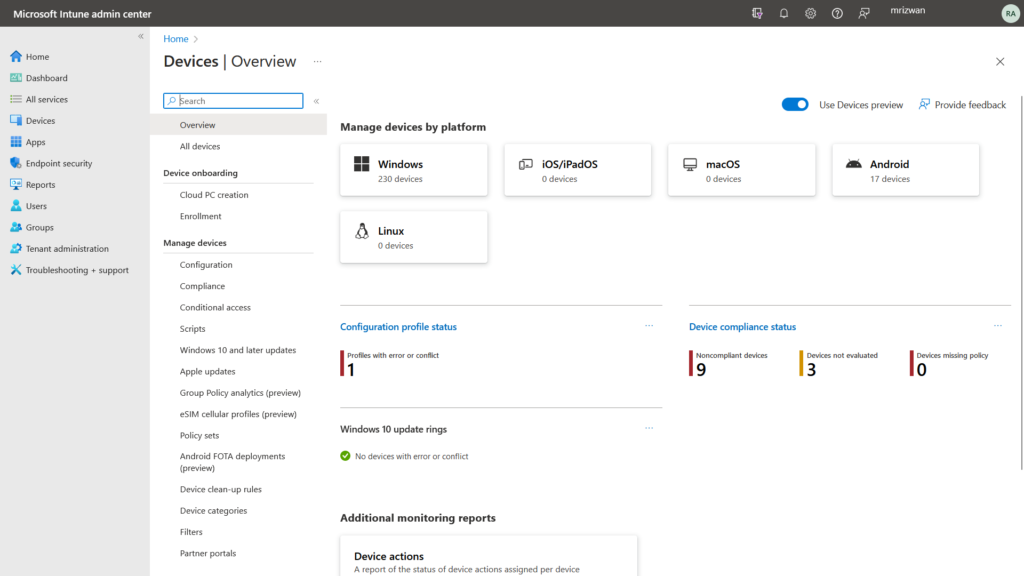
- Device Enrollment: Intune allows administrators to enroll various types of devices, including Windows, iOS, Android, and macOS devices, into the management system.
- Device Configuration: Administrators can enforce device configuration policies (group policies) to ensure devices adhere to corporate standards. This includes settings for passwords, encryption, Wi-Fi, VPN, and many more.
- Compliance Monitoring: Intune enables administrators to monitor the compliance status of devices and enforce compliance policies. This helps ensure that devices adhere to security and regulatory requirements.
- Conditional Access: Administrators can define access policies based on various conditions, such as device compliance, user location, and application sensitivity. This feature helps control access to corporate resources and ensures security.
3. Endpoint Security
Intune helps enhance the security posture of devices by enforcing compliance policies and configurations. It enables features like enforcing password policies, enabling device encryption, and managing device health.
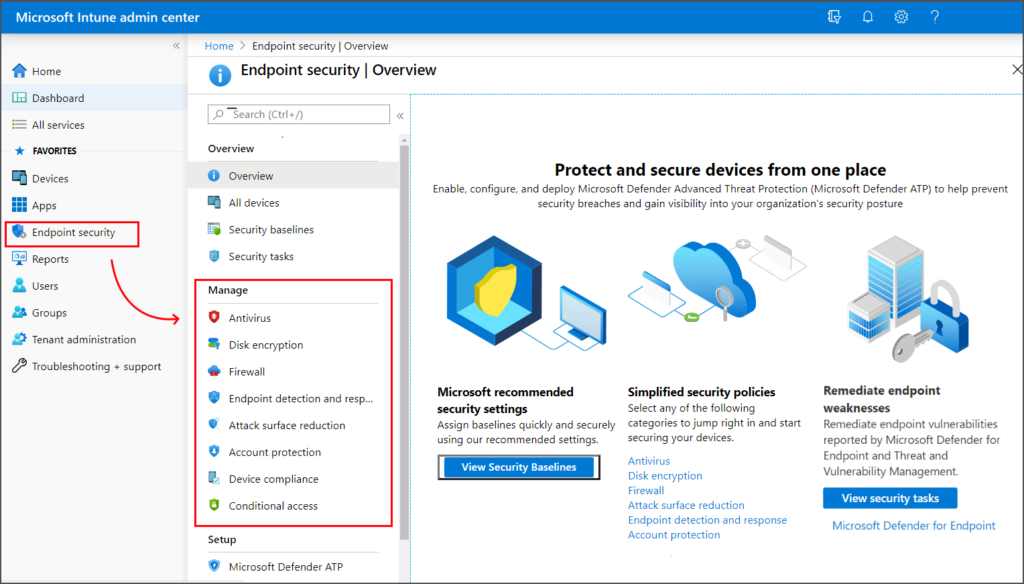
- Data Protection: Intune helps protect corporate data by enforcing policies such as disk encryption, preventing data leakage and allowing data to be remotely wiped from devices if necessary.
- Endpoint Detection and Response: Microsoft Intune does offer Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) capabilities as part of its Endpoint Security features. Intune’s Endpoint Security allows organizations to enhance their security posture by monitoring and responding to threats on managed devices.
- Mobile Threat Defense: Intune integrates with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to provide protection against mobile threats. It helps detect and remediate malware and other malicious activities on managed devices.
4. Mobile Application Management (MAM)
Intune provides app-level protection through its Mobile Application Management (MAM) capabilities. This allows administrators to apply policies and controls to protect corporate data within mobile apps, even on personal devices. It ensures data encryption, prevents data leakage, and enables selective wipe of corporate data.
- App Protection Policies: Intune enables administrators to define policies that apply to specific mobile apps. These policies enforce data protection measures such as encryption, PIN requirements, and data loss prevention (DLP) policies. These policies can be applied to both company-owned and personal devices, ensuring that corporate data is secure.
- App Configuration Policies: App Configuration Policies are a feature of Mobile Application Management (MAM) in Intune that allows administrators to configure and customize settings within managed mobile apps. These policies provide a way to streamline the deployment and management of apps while enforcing specific configurations and preferences.
- App Distribution: Intune provides the capability to distribute and manage mobile apps within the organization. Administrators can deploy apps from various sources, such as public app stores, line-of-business apps, or custom-developed apps. They can also manage app updates, version control, and app assignments to specific users or groups.
Microsoft Intune Reports
Microsoft Intune provides a range of reports that offer insights into device and app management, compliance, security, and overall device health within an organization. These reports help administrators monitor and analyze the status, usage, and performance of managed devices and apps. Here are some key reports available in Microsoft Intune:
- Device Compliance Reports: These reports provide information about the compliance status of devices enrolled in Intune. They show details such as compliant and non-compliant devices, device configurations, and compliance issues. Administrators can use these reports to identify devices that require attention and take necessary actions to enforce compliance policies.
- Windows Updates: With Intune, you can deploy updates to Windows 10/11 devices by using policies for Update rings for Windows 10 and later and Feature updates for Windows 10 and later. To help you monitor and troubleshoot update deployments, Intune supports the following list identifies the columns that are available in the view:
- Devices – The name of the device.
- UPN – Intune user identifier (email).
- Intune Device ID – Intune device identifier.
- AAD Device ID – Azure Active Directory identifier for device.
- Last Event Time – The last time there was new data, or something happened for the device and update.
- Update State – The state of the update for the device. Initial state data is from the service-side, which is the status of the update in the system before it begins to install on the device. When client-side data is available, client-side data is shown, replacing the server-side data.
- Update Substate – A low-level detailed version of the Update State.
- Update Aggregated Status – A high-level summary of the Update State, like In progress or Error.
- Alert Type – When applicable, Alert Type displays the most recent alert message.
- Alert Details – This column isn’t in use.
- Last Scan Time – The last time this device ran a scan for Windows Update.
- Reporting and Analytics: Intune provides reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing administrators to gain insights into device and application usage, compliance status, and security incidents.
Final: Microsoft Intune Features
Most importantly, Microsoft Intune continues to evolve with new features and enhancements regularly. Therefore, we can say that this is not an exhaustive list.



